How To Insert A Catheter In A Female Patient
How To Insert A Catheter In A Female Patient
Urinary catheterization in female patients is a medical procedure performed to drain urine from the bladder when a patient is unable to urinate naturally. It must be done under sterile conditions to prevent infection and ensure patient safety. This guide outlines the general steps for inserting a urinary catheter in a female patient, typically performed by trained healthcare providers.
- Prepare the Equipment
Before beginning the procedure, assemble all necessary sterile supplies:
- Sterile catheter (usually Foley type)
- Sterile gloves
- Lubricating jelly
- Antiseptic solution or wipes
- Sterile drapes
- Urine drainage bag
- Syringe with sterile water for balloon inflation
- Sterile water or saline
- Waste disposal container
Ensure your hands are washed thoroughly and gloves are worn to maintain sterility.
- Position the Patient
Assist the patient into a supine position (lying on her back) with legs bent and knees apart (frog-leg position). Drape the patient properly, exposing only the genital area to maintain privacy and dignity.
- Clean the Perineal Area
Using antiseptic wipes or solution, clean the labia and urethral opening from front to back. Spread the labia with one hand and clean with the other. This step is crucial for preventing urinary tract infections.
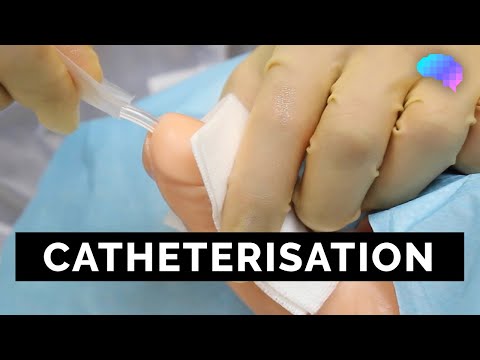
- Lubricate the Catheter
Apply a generous amount of sterile lubricant to the tip and the first few inches of the catheter. This reduces discomfort and allows smooth insertion.
- Insert the Catheter
Gently spread the labia to clearly view the urethral opening. Insert the catheter slowly into the urethra, directing it upward and backward. Advance the catheter until urine begins to flow into the tube.
- Inflate the Balloon
Once urine flows, advance the catheter another 2–3 cm to ensure proper placement. Use the syringe to inflate the balloon with sterile water as instructed (usually 10 mL for adults). This balloon keeps the catheter in place inside the bladder.
- Connect the Drainage Bag
Attach the catheter to the urine drainage bag and position the bag below bladder level. Secure the tubing to the patient’s thigh using tape to prevent tugging or movement.
- Monitor and Document
Check for proper urine flow and patient comfort. Record the procedure in the patient’s chart, noting the time, catheter size, volume of balloon inflation, and any observations.
Also Read: How To Grow Strawberries In Pots
